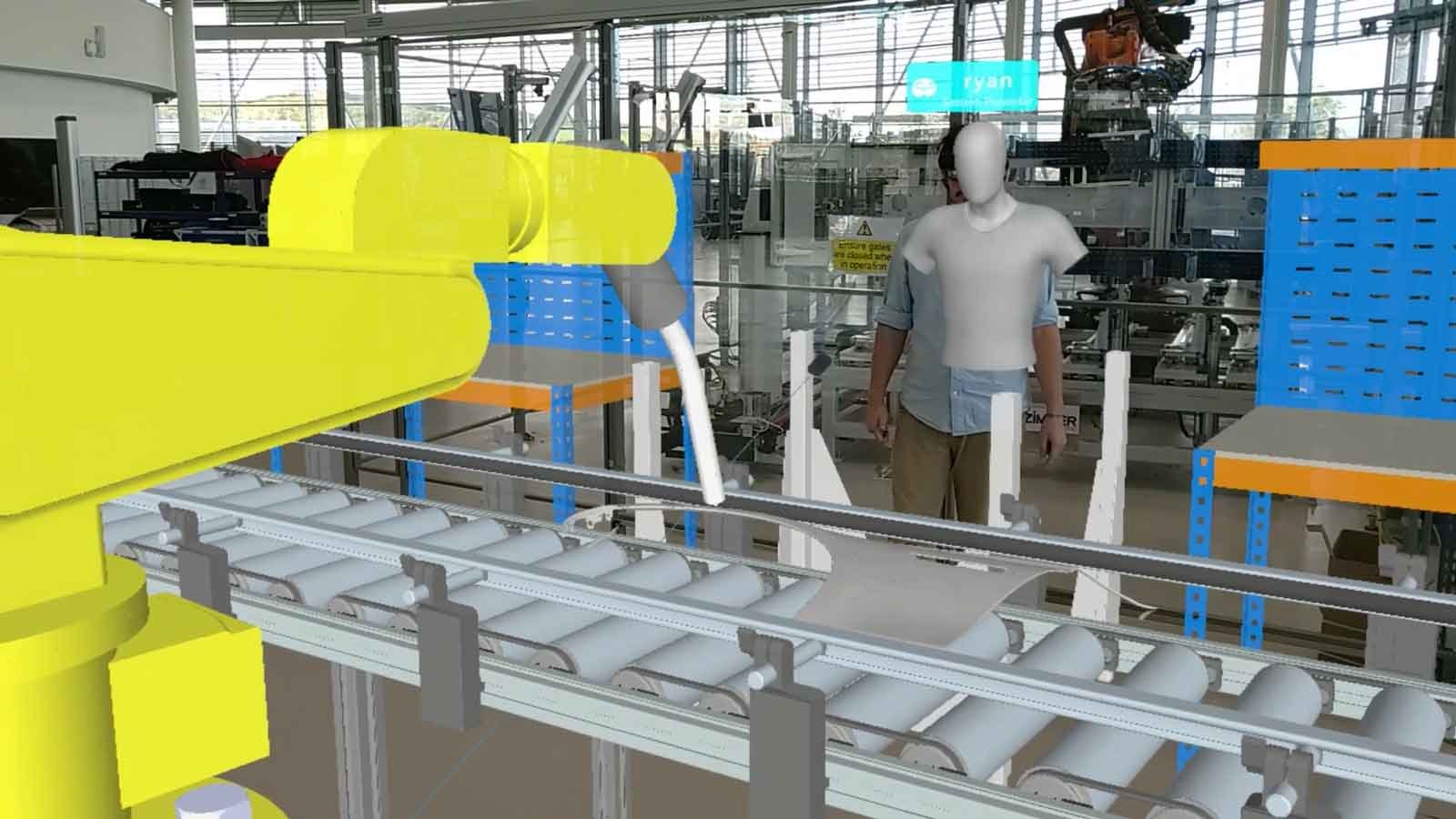
Planning and evaluating a factory layout, whether new, or a refit of an existing site, can be a difficult task due to the scale of the design. It can be hard to visualize the end result from a series of drawings, or viewing large scale 3D content on a 2D screen. Even working in a multi-format environment that combines a mix of scan data, AEC data, CAD Data, metadata etc. can be problematic. Building "mock-ups" from cardboard or foam, can lead to misinterpretation, and miscommunication due to scale, leading to errors, causing delays and producing unnecessary costs.
How can Extended Reality Help?
XR enables users to review their designs in context, and at full scale. By enabling users to collaboratively visualize a design layout using Extended Reality (XR), some of these errors can be highlighted and addressed earlier on in the process, saving companies time and money, and minimizing costly delays and unnecessary travel.
XR enables users to effectively evaluate layouts immersively, ensuring that the final outcome is the most efficient and cost-effective. Using Extended Reality for visualization and layout can enhance and improve a wide range of areas, including:
- Risk assessment processes
- Evaluating traffic flow
- Optimizing the use of space
- Clash detection
- Ensuring machinery is set up to function properly
Which XR devices can be used?
When using Extended Reality for factory layout and planning, there are a variety of devices available that support Augmented, Mixed, or Virtual Reality Technologies. It is important to understand that each technology type benefits specific use cases differently, and each have their own limitations. Users looking to Augmented Reality can take advantage of existing hardware (phone and tablets) for visualization, whereas those looking for a more immersive experience will require Mixed, or Virtual Reality headsets.
Users opting for a Virtual Reality device are immersed in an entirely digital environment. They can navigate a proposed multi-format factory layout at full scale, in a single scene, to evaluate its effectiveness using a number of prebuilt configurations. With the ability to host a collaborative session, users are able to join remotely, from anywhere in the world, or locally, so teams can review the project as it progresses.
Alternatively, Mixed Reality users can lay out a digital version of their factory in their real-world environment. Any proposed changes can be made to the original design data, prepared, optimized, and then reviewed in XR quickly, both locally and collaboratively.
For users who have use cases that suit both Mixed and Virtual reality, there are now devices available that combine the benefits of both. The Meta Quest 3 and Apple Vision Pro are two recently released devices that can switch between Virtual Reality and Mixed Reality using pass-through capabilities. Devices like these allow users to be flexible, enabling them to visualize their layout in a fully digital environment when they need to, while also providing the option to overlay the design in the real world (potentially in the planned location of the factory).

It is important to understand the significance of data preparation for use in the different XR devices. This is particularly true when working with large volumes of data from a variety of sources. Poorly prepared data will result in poor device performance, delivering a poor user experience. It is also important to choose a server-based solution that gives real-time access to digital assets that can dropped in to build the layout from the ground up.
In cases where a site has not yet been selected or built (a greenfield site), XR solutions with offline capabilities can be useful. Areas that have a lot of space are useful when visualizing a full factory layout, but these might not be available when connected to a company’s network. However, by caching models, users can save them to a device to be viewed even when not connected to the network, making offsite working possible. Caching models also enables secure offline access, which may be beneficial for companies with restricted remote access policies.
Early Identification of Issues
Identifying issues early in the design process is a significant factor when trying to minimize delays in the complex process of factory planning and building. Viewing 3D layouts on 2D screens can make it difficult to contextualize and understand the information, which in turn can lead to issues being overlooked. With XR visualization, these issues can be spotted earlier since it enables users to get a better understanding of the layout. Alongside these visualization capabilities, users can also collaborate with other members of the design team to review the factory layout together. Because of this, users can make better informed decisions.
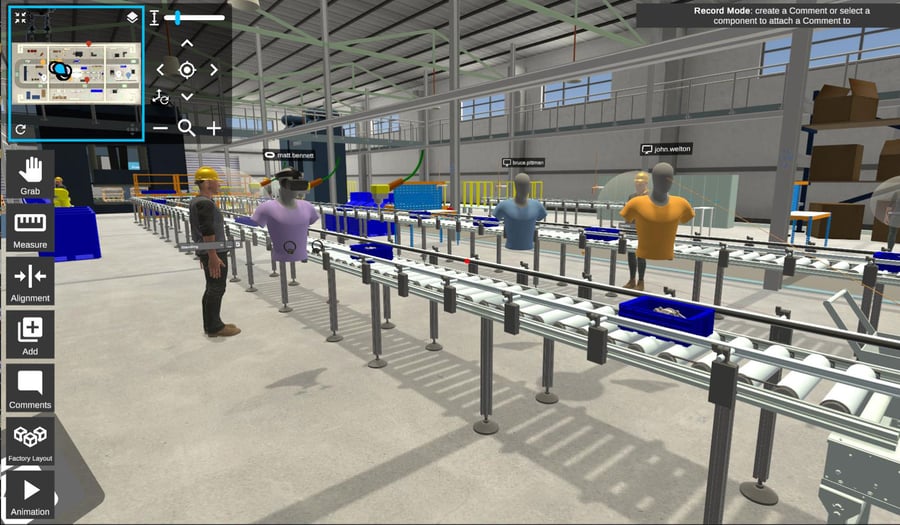

Extended Reality can also be used to test and evaluate potential factory layouts in more detail. Clashes or missing items are easier to spot in XR; but along with this, users can assess human factors and ergonomics. Not only does visualizing in XR make it easier to understand areas people may have issues accessing, but some XR experiences also offer in-built measurement tools, and digital mannequins that can be placed in situ. These mannequins can be used to assess if a person could fit in an area or if an object is in reach, as well as aid in conducting risk assessments. The measuring tools are useful both for verifying that layouts have been set up to specifications and to check that an area is workable.
The capability to effectively plan changes in advance is useful both in situations where a full factory refit is required or when specific machines need to be replaced. When certain machines need to be updated, or have scheduled maintenance, it can be useful to utilize QR codes to precisely place models, or find the component that requires attention. Users can link QR codes with specific models and load them in XR, ensuring that the model appears in the correct spot. As a result, reviewing these layouts and spotting issues is much more efficient, minimizing disruption when it comes to replacing machinery.
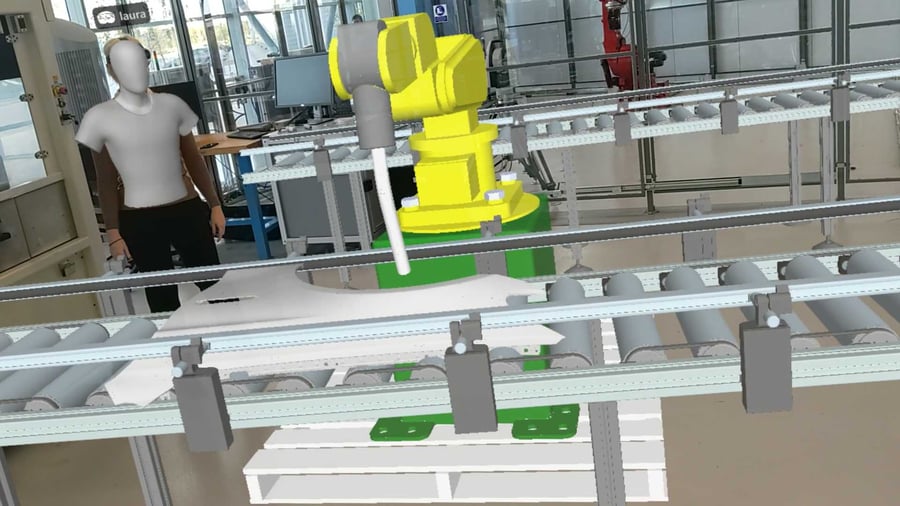
Mixed Reality can be useful when planning a full refit or designing a new layout for a space you have access to. By using Mixed Reality to walk through a physical facility and review a layout before building it, users can significantly reduce the chance of errors in the final stages.
For users having difficulty navigating their large scale designs, waypoints can be incorporated to simplify the process and make walking around a facility in XR much easier. By using waypoints, users can jump between points in a design, making navigating the floor plan much quicker.
Summary
Extended Reality can be incredibly useful when creating factory layout plans. Understanding a large and complex factory layout based only on designs on a 2D computer screen is challenging and can lead to problems being overlooked. With visualization capabilities to review designs at full scale and an in-built tool to help evaluate designs, XR helps users reduce costly errors, identify issues early in the process, and minimize delays.
To learn more about using XR technology for Factory Layout, contact our team of XR specialists today or request a TheoremXR demo to get started today.